Continuous Distributions 5 Example Zero probability for ties with continuous distributions. 1 Discrete Probability Distributions A discrete probability distribution lists each possible value that a random variable can take along with its probability.
Ppt Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions Powerpoint Presentation Id 7057375

Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions Ppt Video Online Download
Pdfs Semanticscholar Org
Structure to include multivariate distributions the probability distributions of pairs of random variables triplets of random variables.
Chapter 6 continuous probability distributions. Probability Distributions and Probability Mass Functions De nition Probability Distribution A probability distribution of a random variable X is a description of the probabilities associated with the possible values of X. Chapter 3 Continuous Random Variables 31 Introduction Rather than summing probabilities related to discrete random variables here for continuous random variables the density curve is integrated to determine probability. Chapter 8 Visualizing data distributions.
Let fx nonnegative be the density function of variable X. Random variables discrete and continuous Probability distributions over discretecontinuous rvs Notions of joint marginal and conditional probability distributions. In other words fxh Px X x h.
The cumulative probability distribution is also known as a continuous probability distribution. Probability is represented by area under the curve. The nobel prize winning psycologist Daniel Kahneman wrote about a.
Convergence in probability Let θbe a constant ε 0 and n be the index of the sequence of RV xn. Let M the maximum depth in meters so that any number in the interval 0 M is a possible value of X. We have already met this concept when we developed relative frequencies with histograms in Chapter 2The relative area for a range of values was the probability of drawing at random an observation in that group.
81 Introduction to Continuous Random Variables. Then fx is the rate at which probability accumulates in the neighborhood of x. The probability is the area under the curve.
In Chapter 5 we will be working with a very important class of continuous random variables called Normal random variables. What kind of distributions are the binomial and Poisson probability distributions. The following things about the above distribution function which are true in general should be noted.
Start studying Chapter 6 Stats. That is the probability that the difference between xnand θis larger than any ε0 goes to zero as n becomes bigger. A Baseball Spinner Game.
Example Number of heads Let X of heads observed when a coin is ipped twice. RS 4 Multivariate Distributions 1 Chapter 4 Multivariate distributions k 2 Multivariate Distributions All the results derived for the bivariate case can be generalized to n RV. In terms of a random experiment this is nothing but randomly selecting a sample of size 1 from a set of numbers which are mutually exclusive outcomes.
What if you want to find the probability for x values that are not integer multiples of the standard deviation. You can give a probability. If a random sample of 15 cash register receipts is selected what is the probability that 10 or more will show that the above three food items were.
For any random variable we might be interested in answering probability questions either exactly or through simulation. For example a set of real numbers is a continuous or normal distribution as. If we discretize X by measuring depth to the nearest meter then possible values are nonnegative integers less.
If limnProbxn- θ ε 0 for any ε 0 we say that xn converges in probability to θ. 62 Joint Probability Mass Function. Px1 x2 xk when the RVs are discrete Fx1 x2 xk when the RVs are continuous.
4 Probability Distributions for Continuous Variables Suppose the variable X of interest is the depth of a lake at a randomly chosen point on the surface. Chapter 8 Continuous Random Variables. Continuous random variables which have infinitely many values can be a bit more complicated.
Satisfying 310 and 311 describes a continuous bivariate probability distribution. Discrete Probability Distributions 158 This is a probability distribution since you have the x value and the probabilities that go with it all of the probabilities are between zero and one and the sum of all of the probabilities is one. A density curve describes the probability distribution of a continuous random variable and the probability of a range of events is found by taking the area under the curve.
Probability Density Functions In Chapter 6 we focused on discrete random variables random variables which take on either a finite or countable number of values. 54 Sampling Distribution of the Mean. In this distribution the set of possible outcomes can take on values in a continuous range.
This is not a law that absolutely must be obeyed but it is the most likely outcome for most probability distributions. 26 Properties of Continuous Probability Density Functions. Calculations are also greatly simpli ed by the fact that we can ignore contributions from higher order terms when working with continuous distri-butions and small intervals.
For example the quality of a high school is sometimes summarized with one number. Recall that a continuous random variable or distribu-tion is defined via a probability density function. The probability density function describes the infinitesimal probability of any given value and the probability that the outcome lies in a given interval can be computed by integrating the probability density function over that interval.
Consider the rand function in the computer software Microsoft Excel. The average score on a standardized test. Continuous probability distributions can be described in several ways.
A typical example for a discrete random variable D is the result of a dice roll. Finding Probabilities for the Normal Distribution The Empirical Rule is just an approximation and only works for certain values. Here the sample space is 123456 and we can think of many different events eg.
The graph of a continuous probability distribution is a curve. Some other pre-requisites eg concepts from information theory linear algebra optimization. You may have noticed that numerical data is often summarized with the average value.
Chapter 2 Appendix B or MLAPP Murphy Chapter 2 for more details Note. This chapter and the previous introduced the notion of a random variable and the associated notion of a probability distribution. Continuous Probability Distributions 193 Section 63.
Schaums Outline of Probability and Statistics 36 CHAPTER 2 Random Variables and Probability Distributions b The graph of Fx is shown in Fig. The joint CDF of X1 X2 Xk will have the form. We show the probability for each pair in the following table.
An alternative description of the distribution is by means of the cumulative. 53 Binomial Probabilities and the Normal Curve. Example The distribution of the order statistics from the uniform.
Usually these questions involve knowledge of the probability distribution. Number of Heads 0 1 2 Probability 14 24 14. Learn vocabulary terms and more with.
52 The Uniform Distribution. Probability Distributions of Discrete Random Variables. Sampling From a Box.
RS Chapter 6 4 Probability Limit plim Definition. Xlength 129 130 131 ywidth 15 012 042 006 16 008 028 004. It can help the intuition to think of a continuous bivariate distribution.
There are 6 possible pairs XY. It has the following properties. 6 Joint Probability Distributions.
A continuous random variable takes on all the values in some interval of numbers. French fries and a drink.

Student Copy Econ 232 Sbe13ch 06 Pptx Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions Chapter Topics Uniform Probability Distribution Normal Course Hero

Chap05 Continuous Random Variables And Probability Distributions

Chapter 6 Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Solutions Textbook Exercises The Random Variable X Is Studocu

Chapter6

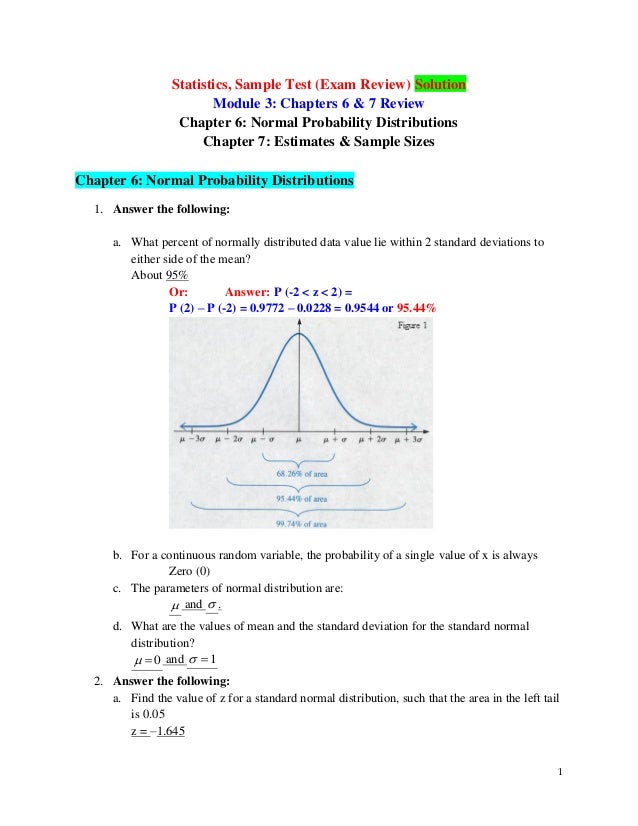
Solution To The Practice Test 3a Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distri

Chapter 6 Continuous Random Variables And Distributions
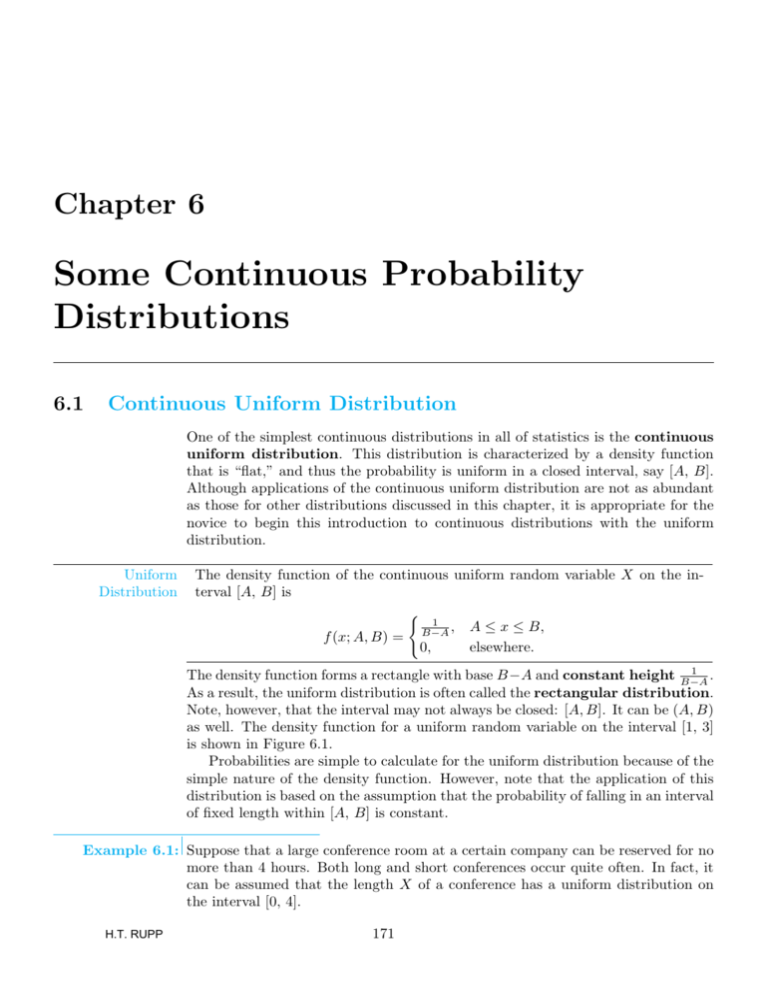
Chapter 6 Some Continuous Probability Distributions

Chapter 6 Discrete Probability Distributions Docsbay